Planning to move your company’s data and worried about losing records, breaking reports, or facing long downtime? That’s exactly why you’re here. ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) gives a clear, repeatable method to pull data from different sources, clean and reformat it, and load it safely into the new system. In this guide you’ll learn how ETL solves real migration problems, which steps to follow, and which tools and checks keep your project on schedule and error-free.
What is data migration in ETL?
Table of Contents
Data migration simply means moving your data from one place to another. But when it comes to business systems, like legacy databases, ERP, CRM, or cloud applications—just moving the data isn’t enough. This is where ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) comes in.
- Extract: Pull data from the source where it currently resides, such as a legacy system or cloud storage.
- Transform: Clean the data, remove duplicates, change formats, and prepare it according to business rules.
- Load: Load the clean and accurate data into the new system or database.
ETL vs Data Migration vs Data Integration
ETL, data migration, and data integration all deal with business data, but each serves a different purpose. Knowing the differences helps you pick the right approach for your projects.
What is ETL in data?
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) is the process of pulling data from source systems, refining it into a usable format, and loading it into a target database or warehouse. Unlike simple migration, ETL ensures data is clean, consistent, and ready for analysis.
What is data migration?
Data migration is the process of moving data from one system, format, or storage location to another. It’s more than just copying files—it’s about ensuring that your information is complete, accurate, and usable in the new environment.
Businesses usually need data migration when they:
- Upgrade from old servers or databases to modern ones
- Switch to cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud
- Consolidate multiple repositories or systems into a single source of truth
- Replace outdated software with new applications (e.g., moving from a legacy CRM to Salesforce)
- Relocate data centers or update IT infrastructure
What is data integration?
Data integration is the process of bringing data from multiple sources together into a single, unified view. Instead of keeping information siloed across CRMs, ERPs, cloud apps, or spreadsheets, integration combines it, cleans it, and prepares it for analysis. This gives businesses one reliable source of truth instead of scattered data across different systems.
The goal of data integration is not just to move data, but to connect and enrich it so teams can extract meaningful insights. Whether it’s combining sales and marketing data to measure ROI, merging healthcare records for better patient care, or linking supply chain and finance systems for smoother operations, integration helps organizations make faster, smarter, and more informed decisions.
Key differences
While ETL, data migration, and data integration are closely related, they serve different purposes:
- ETL (Extract, Transform, Load): Moves data from one or more sources, cleans and transforms it, then loads it into a new system. Best when you need accurate, formatted data ready for analytics.
- Data Migration: Focuses on transferring data from one system or format to another, usually during upgrades, cloud adoption, or consolidation. The goal is safe transfer, not transformation.
- Data Integration: Combines data from multiple sources into a unified view without necessarily moving it permanently. The goal is to break silos and enable better insights.
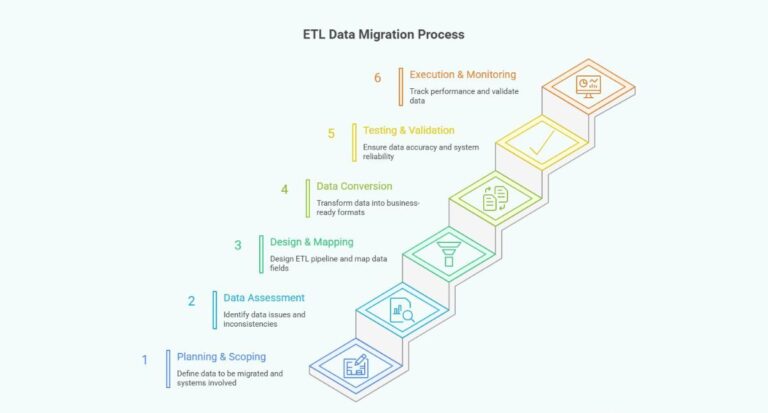
ETL Data Migration Process
Migrating data with ETL isn’t just about moving information. It’s about making sure data is accurate, consistent, and ready for use. Here’s a step-by-step look at how the ETL data migration process works:
Planning & scoping
A strong migration begins with clarity. This phase defines what data will be migrated, which systems are involved, and the expected outcomes. Teams also establish compliance requirements, business continuity needs, and fallback strategies in case of failure. Skipping detailed scoping often leads to scope creep, unexpected costs, and avoidable downtime.
Treat this as a business project, not just a technical one. Include stakeholders from IT, compliance, operations, and business units to avoid surprises.
Data assessment & profiling
Data migrations often expose the “hidden mess” in enterprise data duplicates, missing fields, outdated formats, or inconsistent taxonomies. Profiling your data early helps you understand what you’re dealing with and sets the stage for cleansing and transformation.
A financial services firm found that 15% of its client records had missing identifiers. Profiling flagged these early, allowing cleanup before migration and avoiding potential regulatory penalties.
Design & mapping
Here, the ETL pipeline is designed to decide how data will be extracted from the source, transformed to meet business and compliance rules, and loaded into the target. Mapping ensures every field has a “home” in the new system and defines business logic (e.g., standardizing currencies, merging customer IDs, or reformatting timestamps).
Why it matters: Poorly mapped data often results in orphaned records or reporting errors that cost businesses months to fix after go-live.
Data conversion & transformation
At this stage, raw data is shaped into business-ready information. It goes through cleansing to remove duplicates and errors, standardization to align formats, and enrichment to make it more valuable for decision-making. Legacy structures are also converted into modern formats, whether that means moving from flat files to relational databases or from on-prem systems to cloud warehouses.
Testing & validation
Testing and validation is the biggest step in a data migration project. Testing and validation ensure that migrated data is accurate, complete, and reliable in real-world use. This phase isn’t just about checking numbers. It’s about proving the new environment can support business operations without disruption.
Key activities include:
- Unit testing individual ETL jobs for accuracy and performance.
- System testing to confirm data flows correctly across applications.
- User acceptance testing (UAT) with real stakeholders to validate usability.
- Parallel runs comparing results from legacy and new systems.
Execution & monitoring
This is the last stage where all the preparation pays off. Teams track performance, validate record counts, and flag anomalies in real time, followed by post-migration audits to confirm accuracy and usability. The best practice is to use automated dashboards and have rollback plans ready so any issues can be resolved quickly without disrupting business operations.
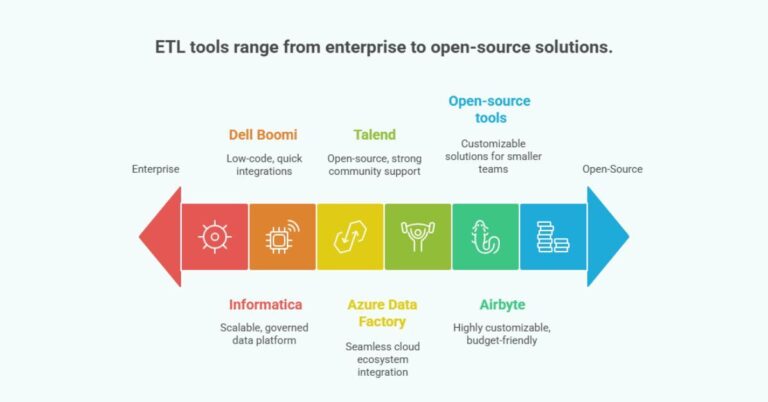
Tools for ETL Data Migration
ETL tools simplify complex migrations by automating extraction, transformation, and loading of data. From enterprise platforms like Informatica and Talend to cloud-native services such as AWS Glue and Azure Data Factory, each tool has unique strengths. The right choice depends on project scale, compliance needs, and budget.
Informatica: A widely used enterprise-grade ETL platform known for scalability and strong data governance features.
Talend: An open-source-friendly ETL tool offering flexibility, cloud integration, and strong community support.
Azure Data Factory: Cloud-native ETL services that integrate seamlessly with their ecosystems, ideal for organizations already using AWS or Azure.
Dell Boomi: Low-code platforms designed for quick integrations and data migrations, especially useful for hybrid IT environments.
Airbyte: Open-source, highly customizable, and budget-friendly. Best for teams that want flexibility and community-driven connectors.
Open-source tools: Options like Hevo, Pentaho, and Apache Nifi provide cost-effective, customizable solutions for smaller teams or those needing flexibility.
Best Practices
Create a solid plan
Define clear objectives, timelines, responsibilities, and risks. By planning every step—what data to move, how to handle dependencies, and how to back up—you minimize surprises and keep the migration on track.
Minimize data input
Review and filter out outdated, duplicate, or irrelevant records before moving them. This reduces workload, cuts storage costs, and ensures the new system isn’t weighed down with “junk” data.
Create a roadmap
A roadmap acts as a blueprint for the migration journey. It lays out phases, dependencies, and milestones, helping teams see the bigger picture while managing the details. With a roadmap, you avoid bottlenecks, communicate progress clearly, and reduce the risk of delays.
Automate wherever possible
By using ETL tools with built-in automation and AI features, you can streamline data cleaning, validation, and transfers. This not only lowers costs but also guarantees accuracy and reliability across your pipeline.
Frequently Asked Questions
Best practices include creating a clear plan and roadmap, minimizing unnecessary data inputs, automating processes where possible, and running thorough testing before going live.
The 5 ETL steps are Extract, Clean, Transform, Load, and Verify together they ensure raw data is collected, refined, converted, moved, and validated for accurate business use.
No, Snowflake is a cloud data warehouse, not a migration tool. However, businesses often migrate data into Snowflake using ETL/ELT tools like Informatica, Talend, or AWS Glue, which handle the extraction, transformation, and loading.