Table of Contents
When businesses upgrade their software or move to the cloud, one of the biggest hurdles they face is transferring existing data safely. If not handled properly, data migration can lead to loss, corruption, or system errors that disrupt operations. This makes many companies view the process as complex and risky. The good news is that with the right planning, tools, and strategy, data migration can be smooth and secure. In this blog, we’ll explore the main types of data migration, common risks, and best practices to ensure a successful transition.
What is Data Migration?
Data migration is the process of moving data from one system to another—whether between storage devices, databases, applications, or from on-premise servers to the cloud. Think of it like shifting books from an old shelf to a new one: everything must be packed, moved, and placed correctly so that nothing is lost or damaged.
The primary goal of data migration is to keep information safe, accurate, and accessible during technology upgrades or system changes. When done properly, it helps organizations modernize their infrastructure while maintaining business continuity.
Why do organizations need Data Migration?
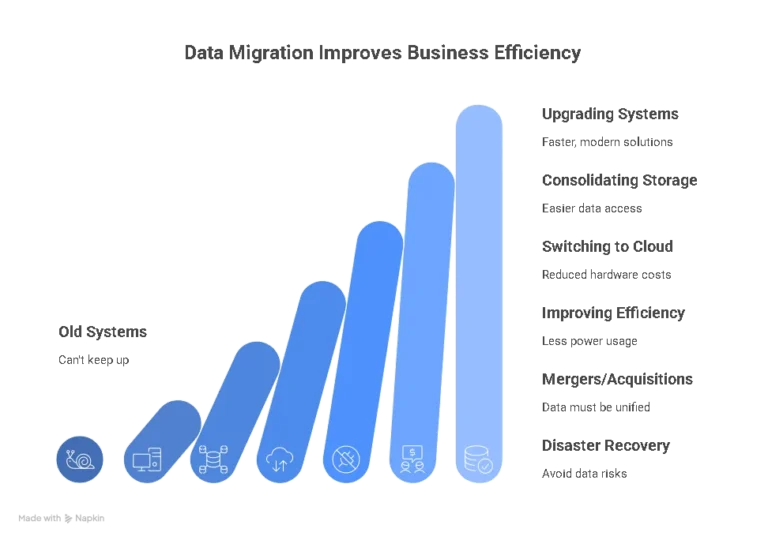
Organizations need data migration whenever their old systems can’t keep up with business needs. Over time, old databases, servers, or storage systems become slow, outdated, or insufficient to meet growing demands. To stay efficient and competitive, companies must migrate their data to more effective platforms. Here are the most common reasons:
Upgrading systems: Replacing legacy databases or servers with faster, modern solutions.
Consolidating storage: Merging scattered data into one central system for easier access.
Switching to the cloud: Reducing hardware costs and gaining flexibility.
Improving efficiency: Moving to systems that use less power and resources.
Mergers or acquisitions: When two organizations combine, their data must be unified.
Disaster recovery readiness: Keeping data in safer environments to avoid risks.
Staying competitive: Adopting new technologies that support innovation and scalability.
4 Main Types of Data Migration
There are four primary types of data transfer, each serving a distinct purpose. Let’s quickly review what they are and when they are used.
Storage Migration
Storage migration refers to the process of transferring data from one storage system to another, typically when a business outgrows its current setup or the hardware becomes outdated. For example, companies may move from traditional HDDs to faster SSDs, or from on-premises servers to cloud storage solutions. The primary objective is to achieve improved speed, reliability, and scalability while reducing overall maintenance costs.
By moving data into modern storage environments, organizations ensure their applications run faster, employees access information more smoothly, and sensitive files stay secure with stronger backup and disaster recovery options.
Database Migration
Database migration refers to the process of transferring data from one database to another, similar to upgrading from an outdated system to a faster, more scalable one.
The primary focus is to ensure data accuracy and usability by maintaining data type compatibility, preserving table relationships, and ensuring transaction consistency during the migration. Done right, it improves performance and supports future growth without disrupting business operations.
Application Migration
Application migration refers to the process of transferring software applications from one environment to another, such as from one operating system to another, from one server to another, or from one cloud platform to another. Since every application has its own data model and dependencies, this process requires extra care to ensure everything functions smoothly after the move.
Key factors to consider include maintaining data format consistency, verifying environmental compatibility, and ensuring that all integrations and configurations continue to function as expected. Proper testing and user transition planning are also critical to avoid downtime or performance issues.
Cloud Migration
Cloud migration refers to the process of transferring data, applications, or entire workloads from on-premises systems to a cloud platform, or even between different cloud providers. It helps businesses gain scalability, flexibility, and often lower costs compared to managing physical infrastructure.
When planning, teams should prioritize security, compliance, performance, and cost management. A successful migration ensures minimal disruption, protects sensitive information, and enables organizations to fully leverage modern cloud capabilities.
Data Migration Process and Strategy
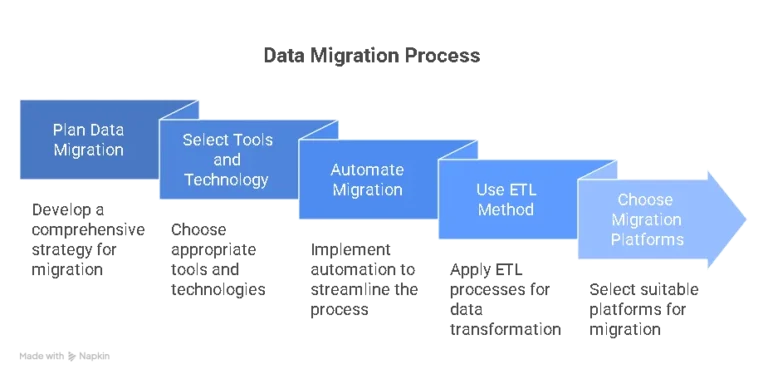
Data migration requires a proper plan, tools, and methods to ensure everything runs smoothly. Selecting the right technology and strategy enables a faster, safer, and less disruptive process for business operations.
Tools and Technology
- Popular tools: Several reliable tools are available to make migrations easier, including AWS Data Migration Service, Azure Migrate, and Google Cloud Data Transfer. These tools reduce manual work and support large, complex projects.
- Data migration automation: Automation helps speed up the process, lowers human errors, and ensures consistency. Automated pipelines can efficiently handle repetitive tasks, such as data validation and synchronization.
- ETL-based data migration: ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) is one of the most used methods. Data is first pulled from the source, then transformed into the right format, and finally loaded into the target system. It ensures data quality and compatibility.
- Data migration platforms: Some widely used platforms include Informatica, Talend, Azure Data Factory, AWS Database Migration Service (DMS), and Google Cloud Dataflow. These platforms help automate workflows, maintain data quality, and support large-scale migrations.
Industry-Specific Use Cases
Professional data migration services are essential across multiple industries, where accuracy, compliance, and security cannot be compromised. Below are some common real-world applications:
Healthcare & EHR Data Migration
Healthcare providers often migrate patient records from outdated Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems to modern platforms. These migrations must be HIPAA-compliant, secure, and error-free to avoid disruptions in patient care. The focus is on safeguarding sensitive data while ensuring doctors and staff have seamless access to records.
Accounting & Financial Data Migration
Financial institutions and businesses frequently transfer transactions, audits, and reports into upgraded accounting software or ERP systems. Here, precision and compliance are critical any inaccuracies can affect audits, tax filings, or financial decision-making. Traceability and data integrity remain the top priorities.
GIS Data Migration
Organizations often migrate geographic datasets, such as maps, spatial layers, and location intelligence, from legacy platforms into advanced GIS solutions like ArcGIS Pro or cloud-based GIS. This migration enables better analysis, integration, and scalability across industries that rely on spatial data.
Insurance & Government Migrations
Both insurance companies and government bodies manage massive volumes of sensitive records, from citizen data to policyholder information. Migration projects in these sectors are typically driven by compliance mandates, digital transformation, or replacing outdated legacy systems. The focus is on ensuring data privacy, meeting regulatory standards, and avoiding service disruptions.
Risks and Common Challenges
Data migration may seem straightforward, but in practice, it presents several risks and challenges. If not handled properly, these challenges can affect business operations, data quality, and even compliance. Below are the most common risks organizations face during migration:
Data Loss and Integrity Issues
One of the biggest risks is losing critical data during the transfer process. Even if data moves, it may lose accuracy, consistency, or formatting, creating gaps and errors in the new system.
Extended Downtime and Business Disruption
Poorly planned migrations can lead to long system outages. This downtime disrupts operations, impacts productivity, and sometimes even affects customer service.
Data Corruption and Compatibility Problems
When source and target systems use different formats, data can become corrupted or unreadable. Compatibility issues often require extra validation and transformation steps.
Application Stability and Performance Risks
Applications connected to migrated data may slow down or crash if dependencies are not mapped correctly, causing performance bottlenecks.
Technical Challenges
Data migration often faces hurdles such as mismatched data formats, complex legacy systems, and large data volumes. Limited tool capabilities and network performance can slow down the process. Without proper expertise and testing, these issues can cause errors, delays, or even failed migrations.
Best Practices for Successful Data Migration
Successful data migration depends on careful planning, smooth execution, and thorough validation to ensure accuracy and minimal disruption.
Plan: Define the migration scope, timelines, and risks. Select the right tools, create backups, and outline the entire process before execution.
Execute: Run the migration in phases, not all at once. This reduces downtime and allows early detection of errors. Keep business-critical systems running smoothly during the process.
Verify: Test and validate the migrated data for accuracy, integrity, and performance. Conduct user acceptance checks and ensure compliance requirements are met before implementing the switch fully.
Choosing the Right Data Migration Partner
Understanding the four main types of data migration is only the first step successful execution requires the right expertise, strategy, and tools. That’s where we come in.
Data Prism specializes in delivering secure, seamless, and scalable data migration services tailored to enterprise needs. Whether you’re modernizing legacy systems, consolidating data into the cloud, or upgrading your data warehouse, our team ensures accuracy, compliance, and minimal downtime.
Data Prism specializes in delivering secure, seamless, and scalable data migration services tailored to enterprise needs. Whether you’re modernizing legacy systems, consolidating data into the cloud, or upgrading your data warehouse, our team ensures accuracy, compliance, and minimal downtime.
FAQ
Manual migration is generally risky as it increases the chances of errors, data corruption, and loss. Automated migration tools and platforms are far more reliable, offering better accuracy, security, and efficiency.
Failures often stem from poor planning, a lack of the right tools, inadequate testing, and underestimating the complexity of the data. These issues can lead to costly errors, downtime, or incomplete transfers.
Nearly every industry relies on data migration at some point. However, it’s most critical in healthcare, finance, insurance, retail, and government sectors where compliance, accuracy, and data security are non-negotiable.